Enforce a Policy
Sentinel is an embedded policy-as-code framework integrated with various HashiCorp products. It enables fine-grained, logic-based policy decisions, and can be extended to use information from external sources. Terraform Cloud enables users to enforce policies during runs.
A policy consists of:
- The policy controls defined as code
- An enforcement level that changes how a policy affects the run lifecycle
This functionality is available in the Terraform Cloud Team & Governance tier, as well as Enterprise. Organization owners can enable a 30-day free trial in their settings under “Plan & Billing”.
Policy sets are a named grouping of policies and their enforcement levels. Each policy must belong to a policy set before it can be evaluated during a run. Each policy set may be applied to specific workspaces, or all workspaces within an organization. Policy sets are the mapping between policies and workspaces.
In this tutorial, you will define a policy set in a version control system (VCS), then connect it to Terraform Cloud to verify that the Terraform version is 0.14.0 and above.
Prerequisites
This tutorial assumes that you are familiar with Terraform Cloud and you have an existing Terraform Cloud workspace configured with AWS access credentials.
You must be in the “owners” team or have “Manage Policies” organization-level permissions to create new policy sets and policies.
Fork GitHub Repository
To create a policy set, you will need a VCS repository to host the policy configuration. Fork the example Enforce Policy repository.
In the repository, you will find two files - sentinel.hcl and allowed-terraform-version.sentinel.
Explore a policy set
sentinel.hcl defines the policy set. This configuration declares a policy named allowed-terraform-version and sets a soft-mandatory enforcement level. You can define multiple policy blocks in the sentinel.hcl file to configure more policies.
policy "allowed-terraform-version" {
enforcement_level = "soft-mandatory"
}Enforcement levels in Terraform Cloud define behavior when policies fail to evaluate successfully. Sentinel provides three enforcement modes.
Hard-mandatory requires that the policy passes. If a policy fails, the run is halted and may not be applied until the failure is resolved.
Soft-mandatory is similar to hard-mandatory, but allows an administrator to override policy failures on a case-by-case basis.
Advisory will never interrupt the run, and instead will only surface policy failures as informational to the user.
Explore a policy
allowed-terraform-version.sentinel defines the policy declared in the policy set. Sentinel code files must follow the naming convention of <policy name>.sentinel.
This policy will pass and return a value of true when the Terraform version is 0.14.0 and above. You can experiment with this policy and trigger a failure by changing the regular expression from ^0\\.14\\.\\d+$ to ^0\\.11\\.\\d+$.
import "tfplan"
main = rule {
tfplan.terraform_version matches "^(0\\.1(4|5)|1\\.0)\\.\d+$"
}Connect the Policy to Terraform Cloud
You need to connect your policy set to your Terraform Cloud organization before you’re able to use it. First, go to your Terraform Cloud’s organization settings by clicking the “Settings” button in the top navigation bar.

Then, click on “Policy Sets” in the left navigation bar.
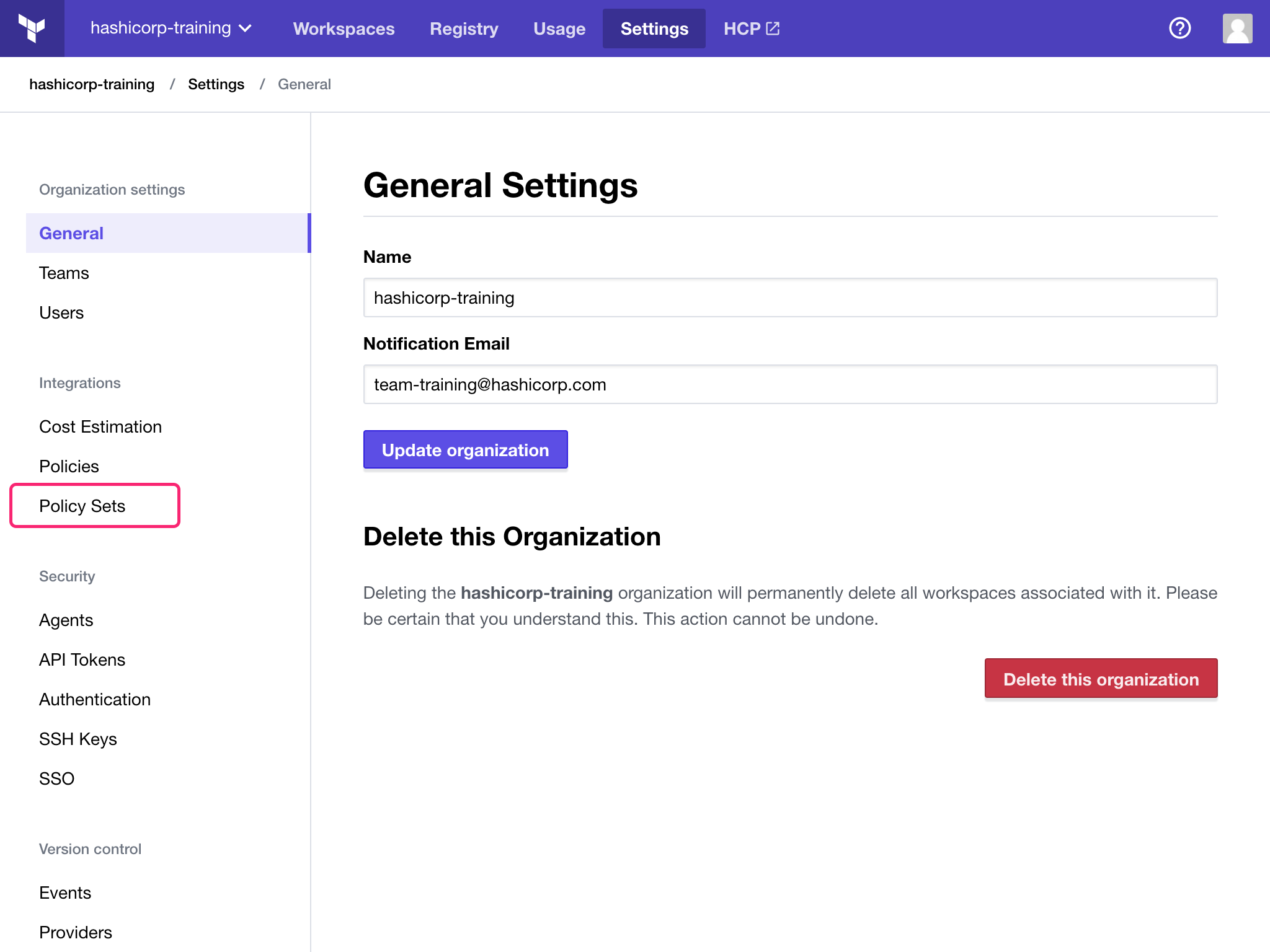
The Policy Sets page lists all existing policy sets. The list will be empty if this is your first policy set. Click on the “Connect a new policy set” button.
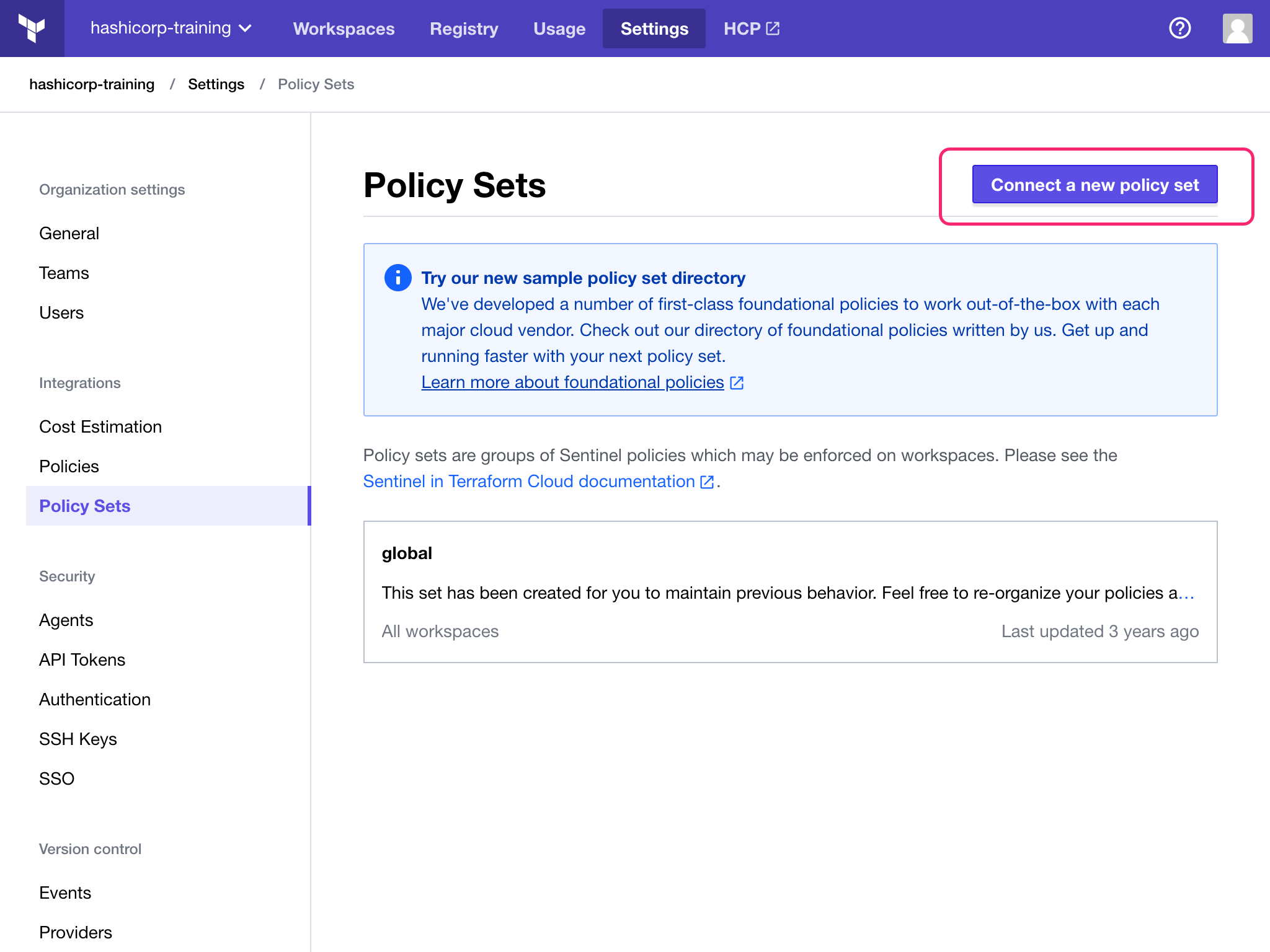
The policy set creation page offers a few options for creating your policy set. Connect to a VCS to source the policy set.
- Select “GitHub” as the VCS provider
- Select your forked repository
- On the “Configure settings” section, under “Scope of Policies”, select “Policies enforced on select workspaces”.
- Specify the workspaces you want this policy to apply to and click the “Add workspace” button to complete adding the workspace to this policy set.
- Finally, click the “Connect policy set” button to create the policy set.
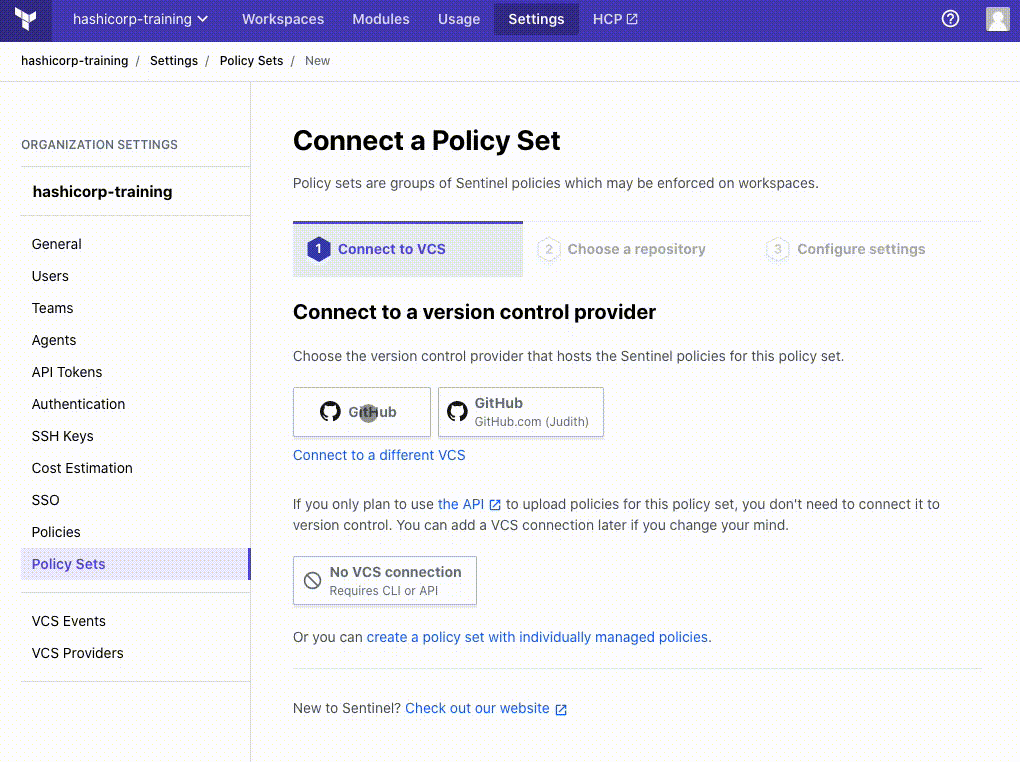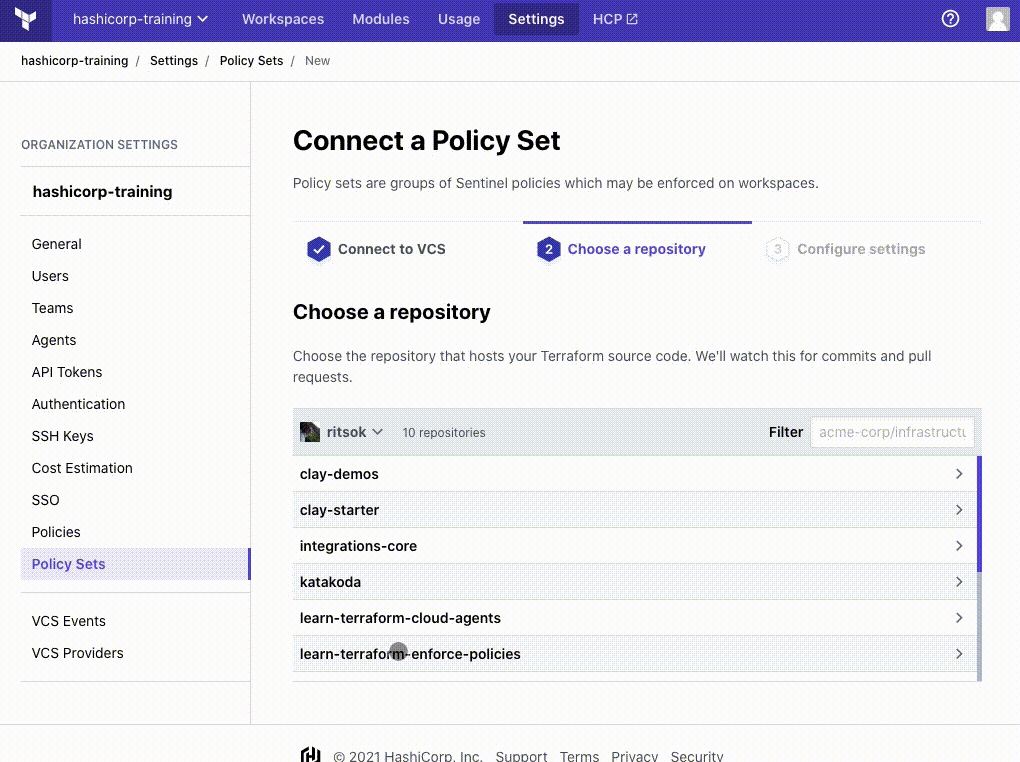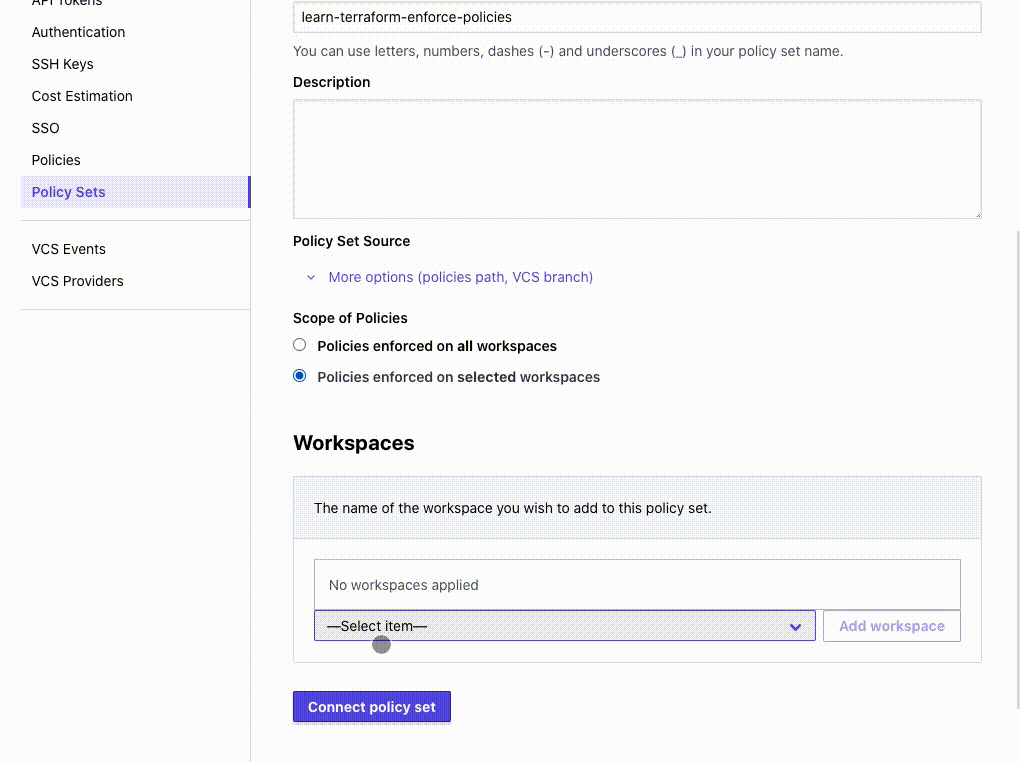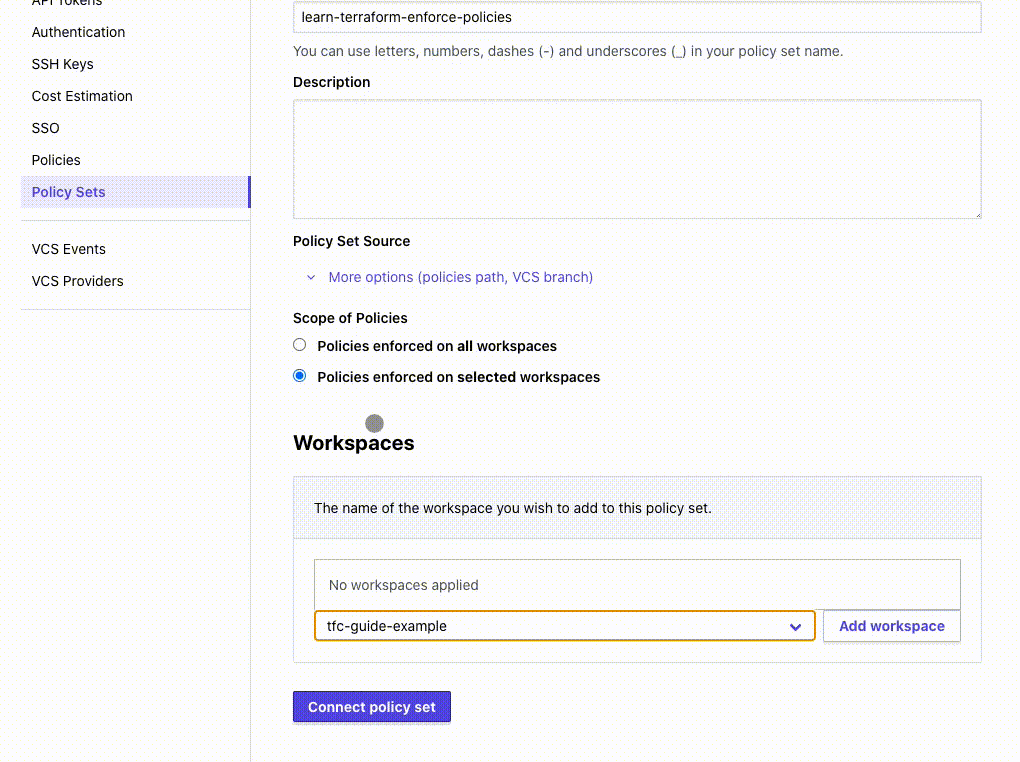
Policy set names within a Terraform Cloud organization must be unique. If your organization already has a policy named learn-terraform-enforce-policies, rename the policy so it’s unique.
This creates a policy set that checks whether the Terraform version is 0 14.0 and above for the workspaces specified.
After creating the policy set, you’ll be taken back to the policy sets index page. The list now contains your new policy set. The VCS information, including the latest commit SHA, should appear within the policy set (if it’s empty at first, allow a few moments and refresh).
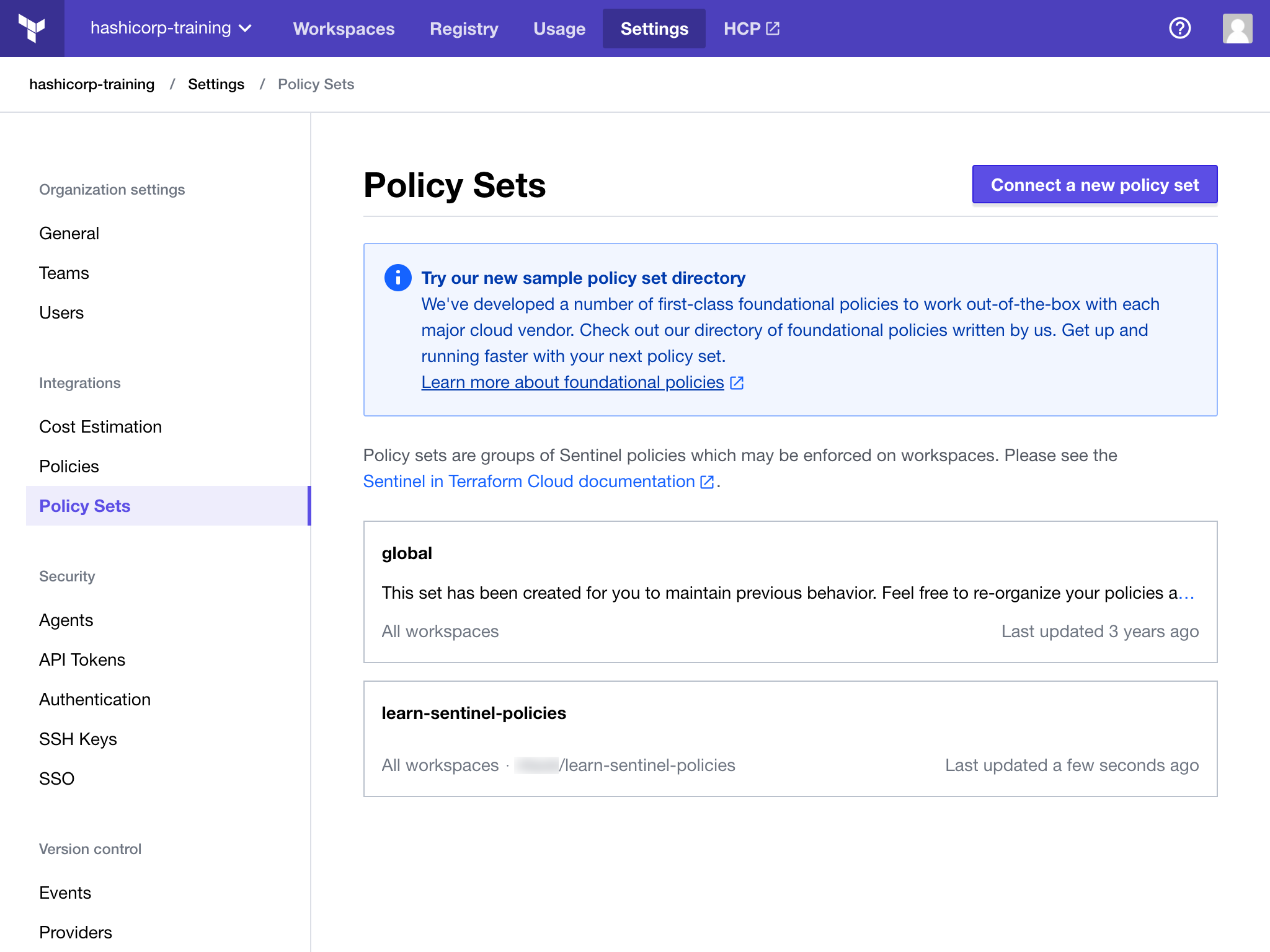
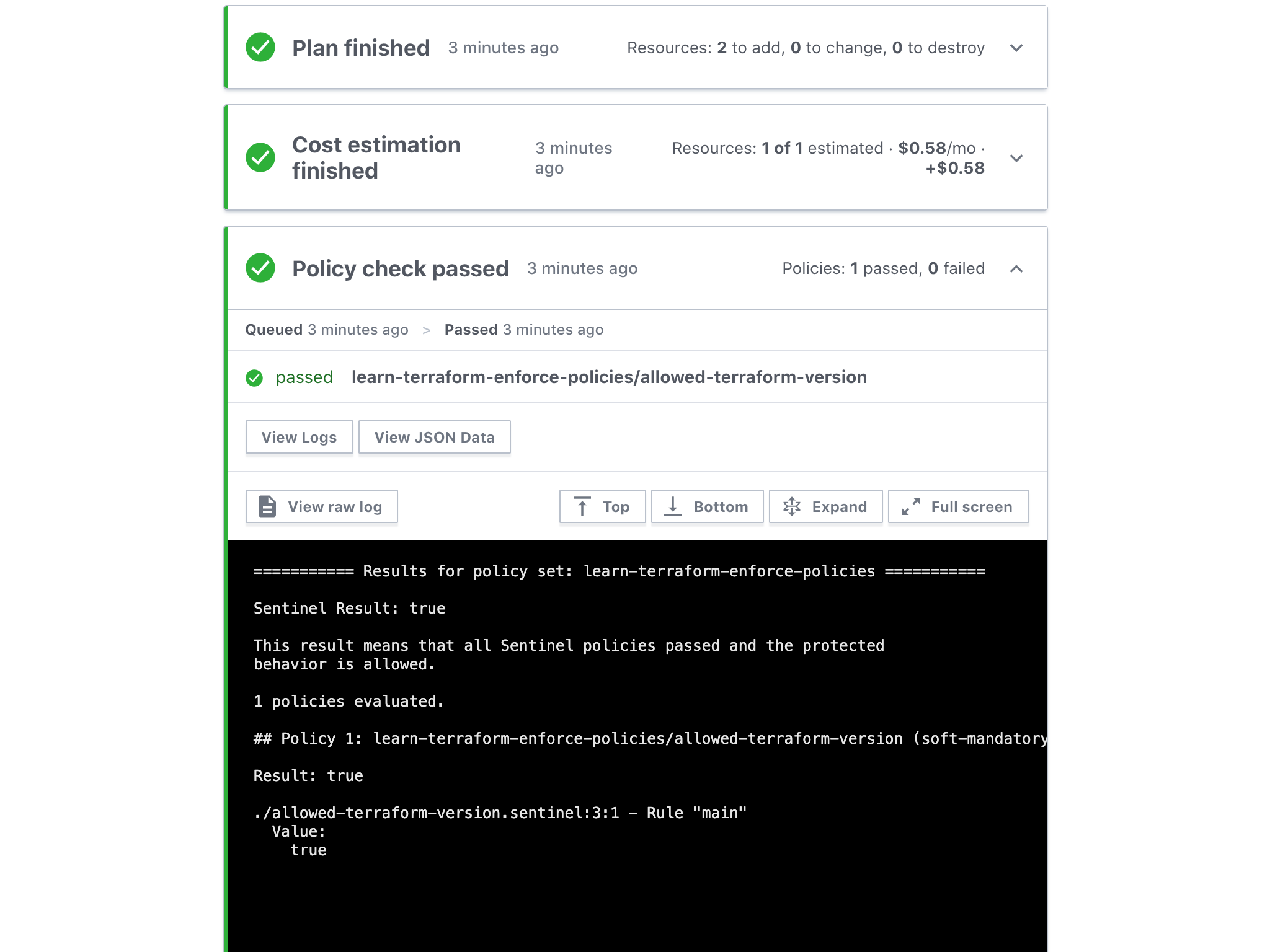
Now that the policy set is configured, navigate to one of the workspaces you selected and queue a new plan. There will now be an additional policy check step in the run, and you should see the allowed-terraform-version policy execute and pass in the output.
Next steps
Congrats — you’ve created and used a policy check to verify the Terraform version before each run.
In the next tutorial, you will learn how to enable and integrate cost estimation into policies. This provides another tool to manage your infrastructure spending.
To learn more about policies, refer to the Terraform Cloud Sentinel documentation.